WordPress and other PHP programs communicate with the server and run scripts using PHP Extensions. Sometimes WordPress and some other scripts will fail to run or cause errors because the required extensions are not enabled.
This article will help you fix that.
To start, log into your Direct Admin account, As shown below, scroll down to the PHP Selector dashboard.

The dashboard will open up to the extensions page, where you can;
1. change the PHP version to the options available on the server.
2. Reset the default PHP settings as per the preset server settings.
3. Enable or disable PHP extensions as required.
Changing your php version. #
If you are accessing this page for the first time the “native” PHP version will be enabled there and you will need to change to the one you want and then save so that you can access the PHP extensions list as shown below.
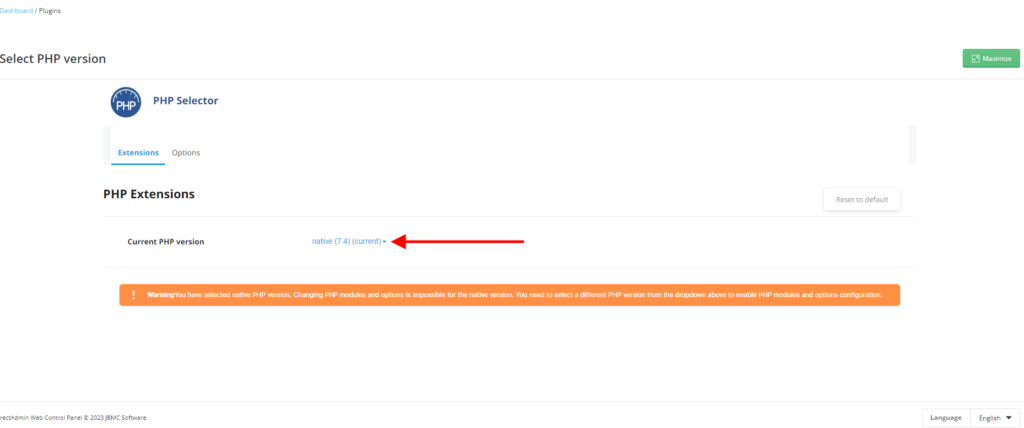
If you want to change the PHP version, please click on the facing down blue arrow as per the image above, then select the PHP version you want as per the picture below.
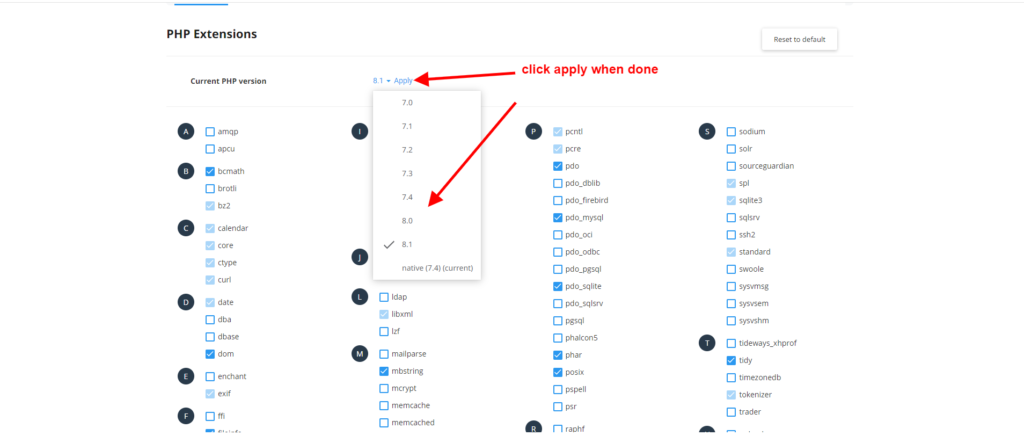
After you have selected the PHP version you want, click on “set as current” or “apply” to activate your new PHP version as per the picture below.
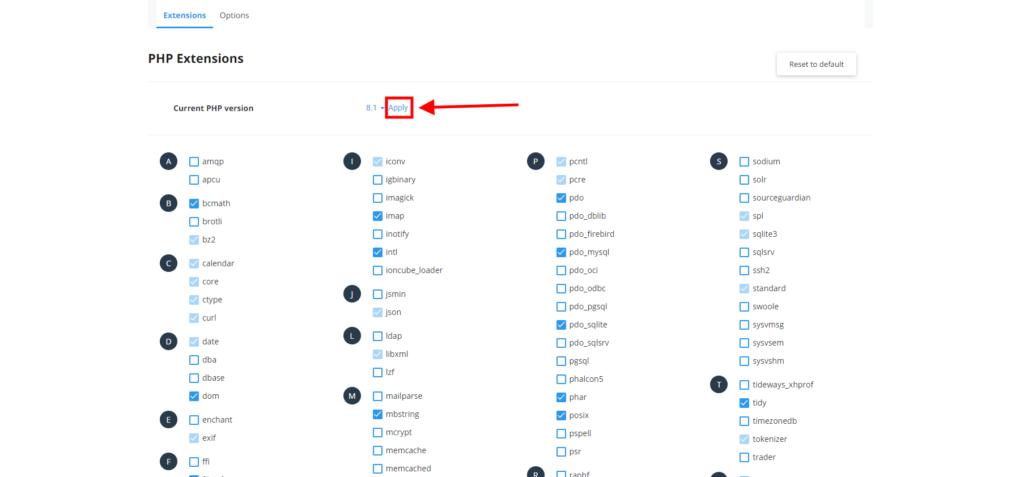
Changing PHP Extentions #
After you have selected the PHP version you want you can now choose the PHP extensions you need, a list of PHP extensions can and their use can be found On this LINK.
If you are using WordPress the basic PHP extensions you need are the following
- APCu
- Dom
- dBase
- fileinfo
- Exif
- Gmagic or Imagick
- IMAP
- json
- mbstring
- mysqli
- pcre
- sodium
- xml
- zip
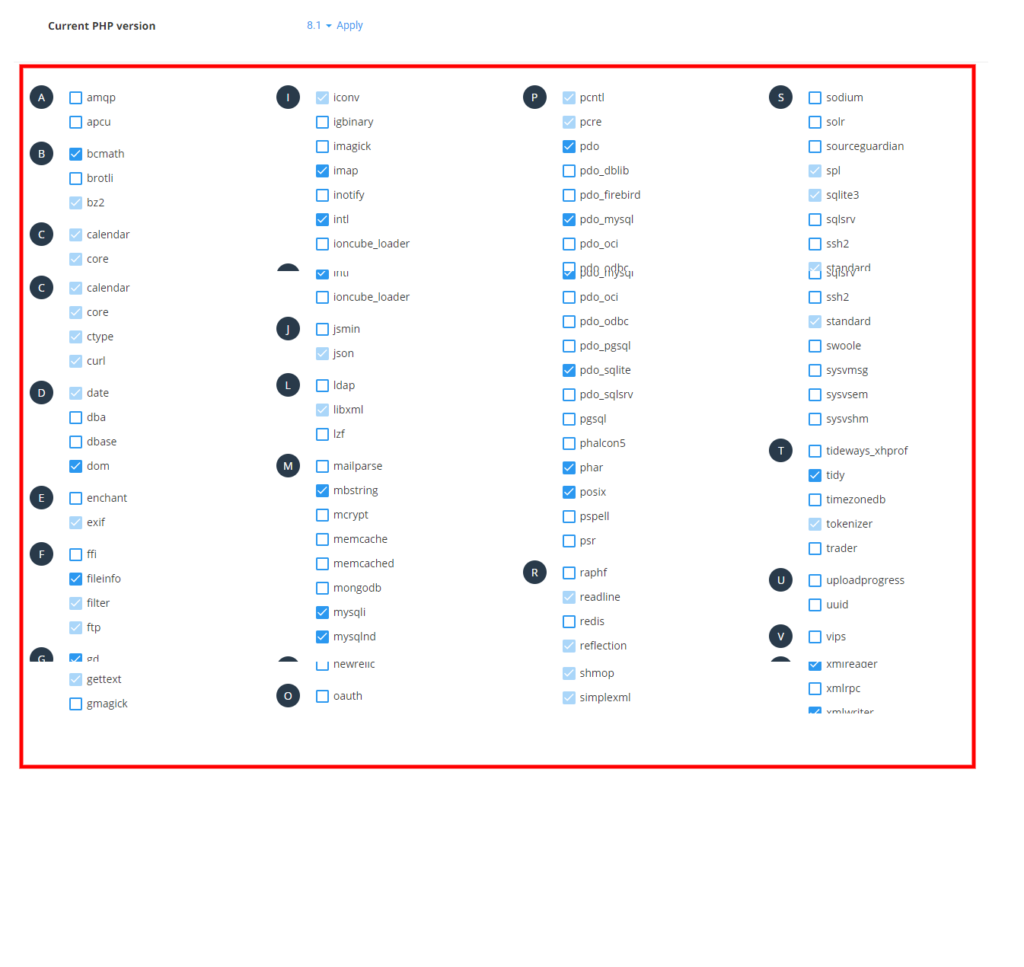
Some themes, plugins and other software / scripts will require other extensions from the basics and you can enable these as required by your vendor by clicking on the module above, remember to select one module at a time , wait until it has activated before electing another.
Changing PHP options and limits #
If you need to change the PHP options and limits you can do so by clicking on the options button as per the picture below.
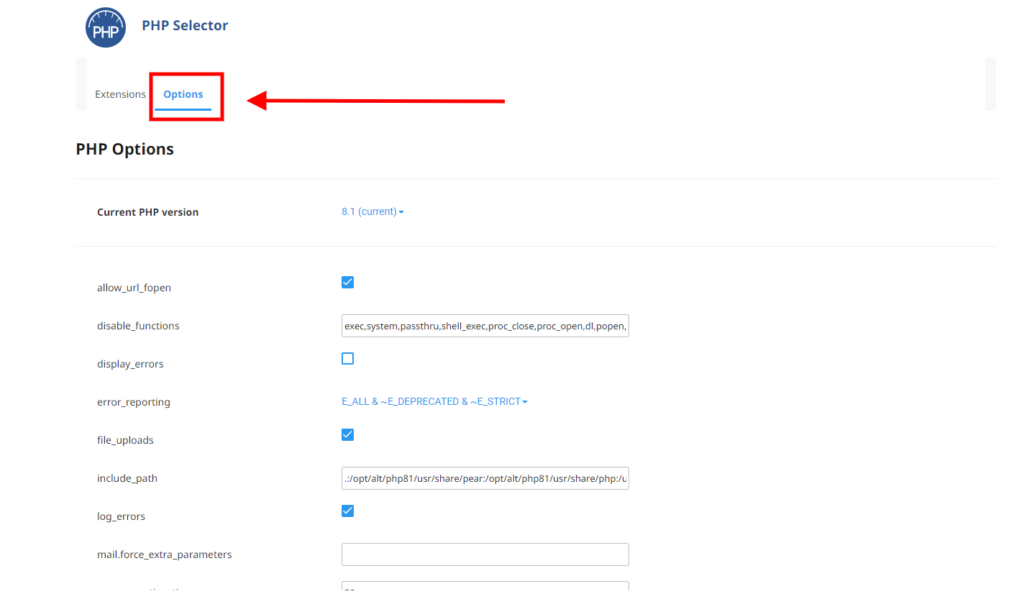
When the allow_url_fopen directive is enabled, you can write scripts that open remote files as if they are local files. For example, you can use the file_get_contents function to retrieve the contents of a web page.
The allow_url_fopen directive is disabled by default. You should be aware of the security implications of enabling the allow_url_fopen directive. PHP scripts that can access remote files are potentially vulnerable to arbitrary code injection.
The disable_functions is used to stop certain PHP functions from executing. There are some PHP functions if gained access to an attacker can do kernel level changes to the server and can make catastrophic effects on the web application. Some vendors however require some of these functions to be enabled for their softwares to work so you can remove them from this line to activate them.
Only remove the one you need and leave the rest as is separated by the comma.
The display_errors setting in PHP is used to determine whether errors should be printed to the screen or not. The error can be used as a part of the output or can be hidden from the user.
Use this when your site is not working correct or throwing errors with numbers and you want to see where the actual error is.
The error_reporting — Sets which PHP errors are reported , you can choose to display all of them or just warnings and suggestions.
Determines whether the PHP errors should be displayed on the screen as part of the output or if they should be shown to the user. Only enable this when your website is having issues and disable it for security reasons when you are done resolving the issue.
Allows file uploading via HTTP
This is the list of directories where scripts look for files (similar to the system’s path variable) . To separate directories, use a colon.
Tells the system whether or not to log errors. Use with caution, if your system is buggy the file can get quite big.
Additional parameters for the mail() function used to send mail.
This sets the maximum time in seconds a script is allowed to run before it is terminated by the parser. This helps prevent poorly written scripts from using up all the resources in the server.
This sets the maximum time in seconds a script is allowed to parse input data, like POST and GET. Timing begins at the moment PHP is invoked at the server and ends when execution begins. The default setting is -1, which means that max_execution_time is used instead.
max_input_vars is a setting which limits the number of inputs / variables you can set when posting forms.
This sets the maximum amount of memory in bytes that a script is allowed to allocate. This helps prevent poorly written scripts for eating up all available memory on a server..
It is a restriction to prevent a hosting package user from accessing any paths on the server that are not authorised, such as the paths to other domains on shared web servers, or to access the hosting software.
The open_basedir function defines the locations or paths from which PHP is allowed to access files using functions like fopen() and gzopen(). If a file is outside of the paths defined by open_basedir, PHP will refuse to open it.
This is the maximum size in bytes that can be posted with the POST method. Typically should not be larger that the upload_max_filezise
The directory where PHP writes session data (files)
The maximum size a file can be uploaded through http




